الحزم تبدأ من
$5000
هل تحتاج إلى مساعدة في اختيار الحزمة المناسبة لرحلتك الطبية؟
بياناتك الصحية محمية معنا
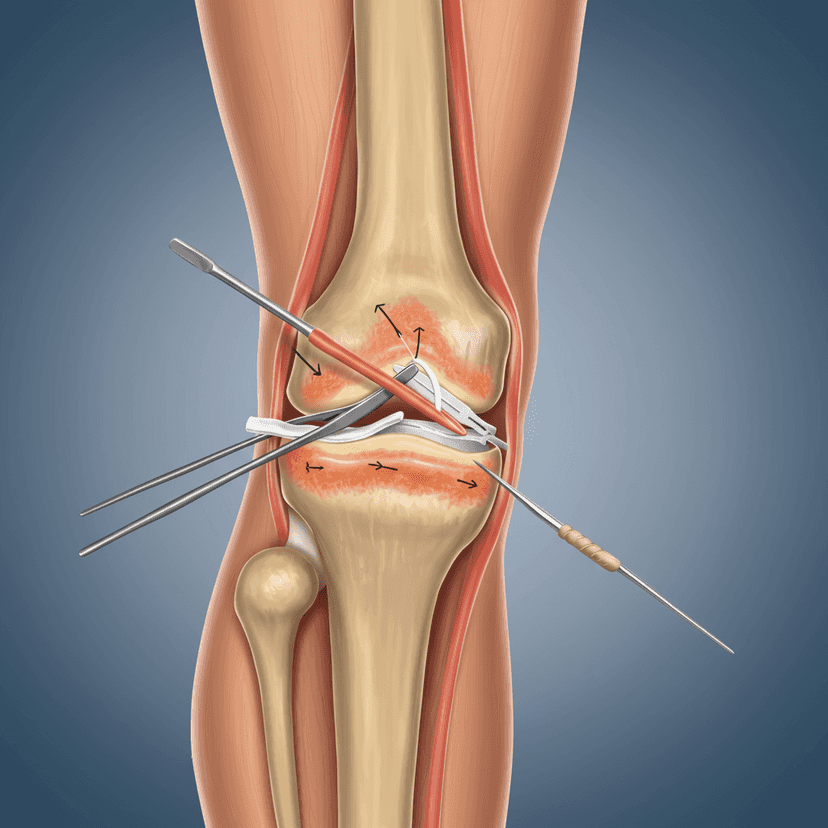
تحويل الحياة بـ عملية إعادة إعمار ACL بالجراحة بالمنظار تليها استئصال الغلاية
إعادة بناء الرباط الصليبي الأمامي بالمنظار متبوعًا باستئصال الغضروف المفصلي هو إجراء جراحي مشترك يستخدم في المقام الأول لمعالجة إصابتين شائعتين في الركبة: تمزق الرباط الصليبي الأمامي (ACL) والأنسجة الهلالية التالفة.
نظرة عامة على الإجراء:
- إعادة بناء الرباط الصليبي الأمامي بالمنظار: يتضمن هذا الجزء من الجراحة استبدال ACL الممزقة مع الكسب غير المشروع ، والتي يمكن أن تكون إما طعم ذاتي (مأخوذة من جسم المريض ، وعادة ما يكون أوتار الركبة أو الوتر الرضفي) أو خيفي (أنسجة المانح). يتم تنفيذ الإجراء بالمنظار ، مما يعني كاميرا صغيرة (منظار المفصل) يتم إدخال الأدوات الجراحية من خلال شقوق صغيرة حول الركبة. وهذا يسمح للجراح برؤية مفصل الركبة والعمل داخله دون إجراء شقوق كبيرة. يتم تأمين الكسب غير المشروع في مكانه مع مسامير أو أجهزة التثبيت الأخرى.
- استئصال الغلبية العصبية: بعد إعادة بناء الرباط الصليبي الأمامي، في حالة تلف الغضروف المفصلي (الغضروف الذي يحيط بالمسافة بين العظام في الركبة) أيضًا، يمكن إجراء استئصال الغضروف المفصلي. يتضمن هذا الإجراء إما إصلاح أو إزالة الغضروف المفصلي الممزق بالكامل أو جزء منه. يعتمد مدى إزالة الغضروف المفصلي على موقع وشدة التمزق. في بعض الحالات، إذا كان التمزق قابلاً للإصلاح، يتم إجراء إصلاح الغضاريف الهلالية بدلاً من ذلك للحفاظ على أكبر قدر ممكن من الأنسجة الطبيعية.
مزايا:
- يؤدي إجراء كلا الإجراءين بالمنظار إلى تقليل تلف الأنسجة وتقليل وقت التعافي مقارنة بالجراحة المفتوحة.
- يساعد كل من إصابات ACL والإصابات في جلسة واحدة في علاج شامل لعدم الاستقرار في الركبة ويمنع المزيد من تدهور المفاصل.
استعادة:
- تتضمن عملية الاسترداد عادةً عدة أسابيع من الشلل تليها العلاج الطبيعي. تركز إعادة التأهيل على استعادة قوة الركبة والمرونة والوظيفة.
- يرتدي المرضى عمومًا دعامة للركبة بعد الجراحة ويستخدمون العكازات للحد من تحمل الوزن على الساق التي أجريت لها العملية.
النتائج:
- هذا النهج المشترك فعال في استعادة استقرار الركبة ومدى الحركة ، وخاصة في المرضى النشطين في الرياضة.
- يمكن أن تؤدي الإدارة الناجحة لكل من إصابات الرباط الصليبي الأمامي والغضروف المفصلي إلى تحسين النتائج على المدى الطويل بشكل كبير وتقليل خطر الإصابة بالتهاب المفاصل العظمي.
يعد هذا الإجراء المزدوج فعالًا جدًا للأفراد الذين يعانون من إصابات الرباط الصليبي الأمامي والغضروف المفصلي، مما يضمن اتباع نهج شامل للتعافي وإعادة التأهيل.
5.0
90% مصنف قيمة مقابل المال
لماذا تختارونا؟
95%
معدل النجاح
0
عملية إعادة إعمار ACL بالجراحة بالمنظار تليها استئصال الغلاية الجراحين
0
عملية إعادة إعمار ACL بالجراحة بالمنظار تليها استئصال الغلاية
0
المستشفيات في جميع أنحاء العالم
0
الحياة التي تم لمسها
نظرة عامة
إعادة بناء الرباط الصليبي الأمامي بالمنظار متبوعًا باستئصال الغضروف المفصلي هو إجراء جراحي مشترك يستخدم في المقام الأول لمعالجة إصابتين شائعتين في الركبة: تمزق الرباط الصليبي الأمامي (ACL) والأنسجة الهلالية التالفة.
نظرة عامة على الإجراء:
- إعادة بناء الرباط الصليبي الأمامي بالمنظار: يتضمن هذا الجزء من الجراحة استبدال ACL الممزقة مع الكسب غير المشروع ، والتي يمكن أن تكون إما طعم ذاتي (مأخوذة من جسم المريض ، وعادة ما يكون أوتار الركبة أو الوتر الرضفي) أو خيفي (أنسجة المانح). يتم تنفيذ الإجراء بالمنظار ، مما يعني كاميرا صغيرة (منظار المفصل) يتم إدخال الأدوات الجراحية من خلال شقوق صغيرة حول الركبة. وهذا يسمح للجراح برؤية مفصل الركبة والعمل داخله دون إجراء شقوق كبيرة. يتم تأمين الكسب غير المشروع في مكانه مع مسامير أو أجهزة التثبيت الأخرى.
- استئصال الغلبية العصبية: بعد إعادة بناء الرباط الصليبي الأمامي، في حالة تلف الغضروف المفصلي (الغضروف الذي يحيط بالمسافة بين العظام في الركبة) أيضًا، يمكن إجراء استئصال الغضروف المفصلي. يتضمن هذا الإجراء إما إصلاح أو إزالة الغضروف المفصلي الممزق بالكامل أو جزء منه. يعتمد مدى إزالة الغضروف المفصلي على موقع وشدة التمزق. في بعض الحالات، إذا كان التمزق قابلاً للإصلاح، يتم إجراء إصلاح الغضاريف الهلالية بدلاً من ذلك للحفاظ على أكبر قدر ممكن من الأنسجة الطبيعية.
مزايا:
- يؤدي إجراء كلا الإجراءين بالمنظار إلى تقليل تلف الأنسجة وتقليل وقت التعافي مقارنة بالجراحة المفتوحة.
- يساعد كل من إصابات ACL والإصابات في جلسة واحدة في علاج شامل لعدم الاستقرار في الركبة ويمنع المزيد من تدهور المفاصل.
استعادة:
- تتضمن عملية الاسترداد عادةً عدة أسابيع من الشلل تليها العلاج الطبيعي. تركز إعادة التأهيل على استعادة قوة الركبة والمرونة والوظيفة.
- يرتدي المرضى عمومًا دعامة للركبة بعد الجراحة ويستخدمون العكازات للحد من تحمل الوزن على الساق التي أجريت لها العملية.
النتائج:
- هذا النهج المشترك فعال في استعادة استقرار الركبة ومدى الحركة ، وخاصة في المرضى النشطين في الرياضة.
- يمكن أن تؤدي الإدارة الناجحة لكل من إصابات الرباط الصليبي الأمامي والغضروف المفصلي إلى تحسين النتائج على المدى الطويل بشكل كبير وتقليل خطر الإصابة بالتهاب المفاصل العظمي.
يعد هذا الإجراء المزدوج فعالًا جدًا للأفراد الذين يعانون من إصابات الرباط الصليبي الأمامي والغضروف المفصلي، مما يضمن اتباع نهج شامل للتعافي وإعادة التأهيل.















