Charting the Course of Your Heart: ECG Testing Explained
14 Sep, 2023
 Healthtrip
HealthtripYour heart, a remarkable organ, tirelessly pumps blood throughout your body, ensuring that oxygen and nutrients reach every cell. To monitor the health of this vital organ, medical professionals often turn to an Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) test. This simple yet powerful diagnostic tool provides valuable insights into your heart's electrical activity, aiding in the early detection and management of various heart conditions. In this blog, we'll delve into the world of ECG testing, exploring its significance, procedure, and the crucial information it can reveal.
1.Understanding the ECG Test
- The Basics of ECG:
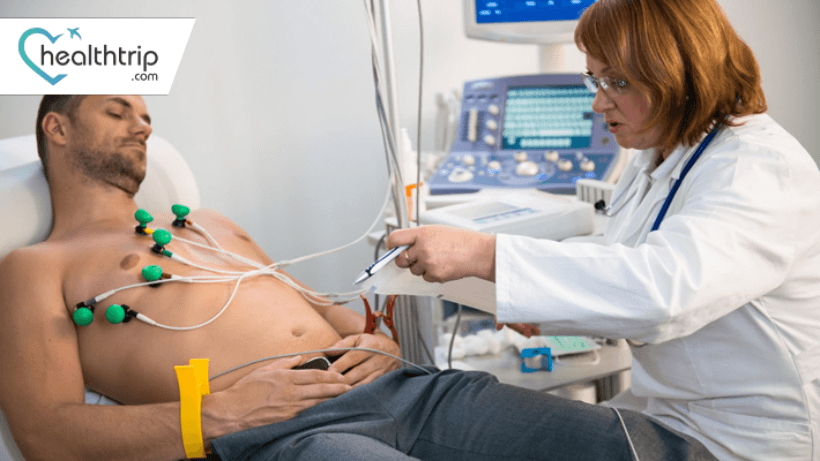
An ECG is a non-invasive test that records the electrical signals produced by your heart as it beats. It does so by placing small, adhesive electrodes on your skin at various points across your chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes are connected to a machine that produces a graph, known as an electrocardiogram, showcasing the electrical impulses generated by your heart.
- Why Is It Done?
ECGs serve multiple purposes, including diagnosing heart conditions, assessing the effectiveness of treatments, and monitoring overall heart health. Some common reasons for undergoing an ECG include chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and as part of a routine checkup.
- Types of ECGs:
There are various types of ECGs, each designed for specific purposes:
- Resting ECG: This is the standard ECG performed while you're at rest, providing a baseline reading of your heart's electrical activity.
- Stress ECG: Also known as a treadmill or exercise ECG, this test measures your heart's response to physical exertion, helping diagnose coronary artery disease and other exercise-related heart problems.
- Holter Monitor: This portable device records your heart's activity continuously over 24 to 48 hours, helping detect irregularities that may not show up during a brief ECG.
2.What Does It Reveal?
An ECG can provide crucial information about your heart's health, including:- Heart Rate: The number of heart beats per minute.
- Heart Rhythm: Whether your heart is beating regularly or irregularly.
- Heart Axis: The direction in which electrical impulses travel through your heart.
- Heart Enlargement: Indications of an enlarged heart.
- Ischemia: Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, a sign of coronary artery disease.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
- Conduction Disorders: Problems with the electrical pathways in your heart.
3.Benefits of ECG Testing
- Early Detection: ECGs can detect heart problems at an early stage, even before symptoms appear. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and can prevent serious complications.
- Monitoring Chronic Conditions: Individuals with existing heart conditions, like arrhythmias or heart disease, can benefit from regular ECG monitoring to track their condition's progression and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
- Risk Assessment: ECGs can help determine an individual's risk of heart disease or stroke, allowing for preventive measures to be taken.
- Safety: ECGs are non-invasive and generally safe, making them suitable for individuals of all ages
4.ECG Test Procedure:
- Preparation:
- You may be asked to wear a gown, or you might need to remove your shirt or blouse to access the areas where the electrodes will be placed.
- Men may need to remove chest hair in the electrode placement areas to ensure good contact.
- Inform the healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as some drugs can affect heart rate or rhythm.
- Placement of Electrodes:
- The technician or healthcare provider will place small, adhesive electrodes (usually 10 in total) on specific areas of your body. These typically include the chest, arms, and legs. The exact placement may vary depending on the type of ECG being performed.
- Electrodes are attached to the skin with a mild adhesive, and they may feel slightly cold when applied.
- Electrode Lead Wires:
- Once the electrodes are in place, lead wires are connected to each electrode. These wires transmit the electrical signals from your heart to the ECG machine.
- The lead wires are color-coded and correspond to specific areas of the heart.
- Recording:
- You will be asked to lie still and relax. It's important to remain as calm as possible during the test, as stress or anxiety can affect the results.
- The ECG machine records the electrical activity of your heart as it beats. The process typically takes a few minutes.
- The technician or healthcare provider will monitor the machine to ensure that a clear, accurate recording is obtained.
- Completion:
- Once the ECG recording is complete, the electrodes and lead wires will be removed.
- You can usually return to your regular activities immediately after the test, and there is typically no recovery time required.
- Interpretation:
- The recorded data is then analyzed by a healthcare provider, often a cardiologist, who interprets the results.
- They will look for patterns, abnormalities, and irregularities in the heart's electrical activity.
- Results and Follow-up:
- The ECG results will be discussed with you by your healthcare provider. Depending on the findings, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
- If the ECG is part of a routine checkup and no significant issues are found, your healthcare provider may simply review the results with you to ensure your heart health.
5.Advancements in ECG Technology
- Digital ECGs: Traditional ECGs involved paper tracings that required manual interpretation. Nowadays, digital ECG machines are the norm, allowing for quicker data acquisition, storage, and analysis. These digital ECGs can also be easily transmitted electronically to specialists for remote consultations.
- Mobile ECG Devices: The rise of wearable technology has given birth to portable ECG devices that individuals can use at home. These devices, like smartwatches equipped with ECG capabilities, provide a convenient way to monitor heart health regularly.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have entered the realm of ECG analysis. AI algorithms can help detect subtle abnormalities in ECGs that might be missed by human observers, improving accuracy and efficiency in diagnosis.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Continuous ECG monitoring devices, such as implantable loop recorders, offer long-term insights into heart activity. These are particularly useful for diagnosing intermittent arrhythmias or unexplained fainting spells.
6.Future Possibilities
- Personalized Medicine: With advances in genomics and data analysis, ECGs could play a pivotal role in personalized medicine. By combining genetic information with ECG data, doctors might tailor treatments more precisely to an individual's unique cardiovascular profile.
- Remote Monitoring: Telemedicine is on the rise, and ECGs could become an essential component of remote healthcare. Patients could perform ECG tests at home, with the data transmitted to healthcare providers for real-time assessment.
- Preventive Screening: As ECG technology becomes more accessible, routine screening for heart conditions may become more widespread. This proactive approach could help catch heart issues at their earliest stages, reducing the burden of heart disease.
- Integration with Other Health Data: ECGs are just one piece of the puzzle. In the future, they may be integrated with data from other wearable sensors and health records to provide a comprehensive view of an individual's health.
Most popular procedures in India
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
Related Blogs

Top 5 Heart Surgeons in Krefeld
Find expert cardiology specialists in Krefeld, Germany recommended by HealthTrip.
Top 10 Cardiology Hospitals in Krefeld
Discover the leading cardiology hospitals in Krefeld, Germany with HealthTrip.
Top 5 Heart Surgeons in Berlin
Find expert cardiology specialists in Berlin, Germany recommended by HealthTrip.

Top 10 Cardiology Hospitals in Berlin
Discover the leading cardiology hospitals in Berlin, Germany with HealthTrip.

Top 5 Heart Surgeons in Schwerin
Find expert cardiology specialists in Schwerin, Germany recommended by HealthTrip.

Top 10 Cardiology Hospitals in Schwerin
Discover the leading cardiology hospitals in Schwerin, Germany with HealthTrip.










