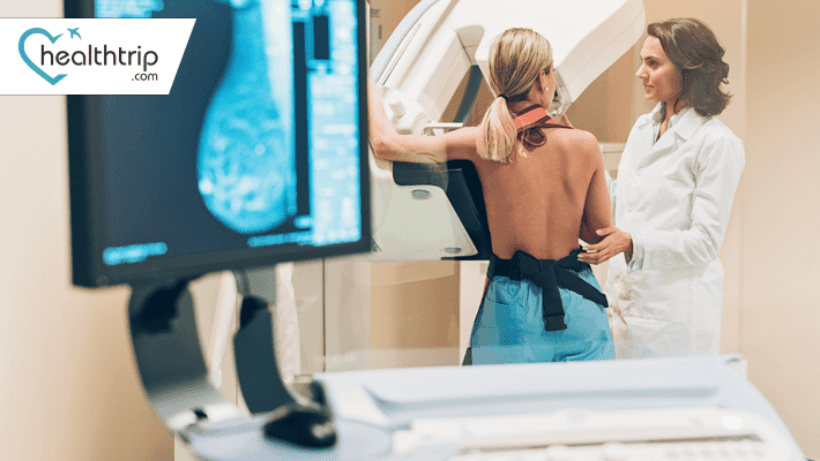

Breast Biopsies in the UAE: Your Roadmap to Early Cancer Diagnosis
30 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip
HealthtripWhen it comes to women's health, breast cancer remains a significant concern. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, and one of the critical steps in diagnosis is a breast biopsy. Understanding breast biopsies is essential for both patients and their healthcare providers to make informed decisions. In this blog, we will delve into the world of breast biopsies, exploring the different types, reasons for conducting them, the procedure itself, and what the results mean.
The Importance of Breast Biopsies
Breast biopsies are a crucial tool in diagnosing breast abnormalities. They are performed to determine if a lump, mass, or suspicious area in the breast is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). A biopsy is often the definitive method for distinguishing between these possibilities. The information gained from a breast biopsy guides the treatment plan, providing a solid foundation for decisions on surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other treatments.
Most popular procedures in India
1. Early Detection
One of the primary reasons breast biopsies are so crucial is their role in early detection. Breast cancer, when caught in its early stages, is more treatable and often associated with better outcomes. Biopsies are used to distinguish between benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) breast abnormalities. When a biopsy identifies cancer, it allows for timely initiation of treatment, which can be life-saving.
2. Tailored Treatment Plans
Breast biopsies provide vital information that guides treatment decisions. The type of breast cancer, its stage, and other characteristics revealed through the biopsy results help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to the individual patient. This ensures that the chosen treatment options are appropriate, effective, and minimize the potential for unnecessary interventions.
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
3. Reducing Unnecessary Interventions
On the other hand, when a breast biopsy determines that an abnormality is benign, it can provide peace of mind to patients and prevent unnecessary surgeries or treatments. Avoiding unnecessary interventions is not only beneficial for a patient's physical and emotional well-being but also helps reduce healthcare costs.
4. Evaluation of Other Breast Conditions
Breast biopsies are not limited to cancer diagnosis. They are also performed to assess various breast conditions, such as atypical lesions, fibroadenomas, or infections. Identifying the nature of these conditions through biopsy is essential for appropriate management and follow-up.
5. Research and Advancements
Biopsy samples contribute to ongoing research and advancements in the field of breast cancer. They help researchers better understand the disease, its variations, and potential treatment options. This research ultimately leads to improved diagnostic techniques and treatment strategies, benefiting current and future breast cancer patients.
6. Informed Decision-Making
For patients, understanding the results of a breast biopsy is empowering. It enables them to actively participate in their healthcare decisions, discuss treatment options with their healthcare providers, and seek second opinions when needed. Informed decision-making is essential in managing breast health effectively.
Reasons for Conducting a Breast Biopsy
Breast biopsies are performed for various reasons, all of which are aimed at determining the nature of breast abnormalities. These abnormalities may be discovered through screening, physical examination, or when a patient experiences specific breast-related symptom. Understanding the reasons for conducting a breast biopsy is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. In this section, we will explore the primary motivations behind recommending breast biopsies.
1. Palpable Lumps
One of the most common reasons for conducting a breast biopsy is the presence of palpable lumps or masses in the breast. These lumps can be discovered by the patient during a self-exam or by a healthcare provider during a clinical breast examination. A biopsy is essential to distinguish between benign and malignant lumps, as it can be challenging to determine the nature of a lump through physical examination alone.
2. Imaging Abnormalities
Abnormal findings on breast imaging studies such as mammograms, ultrasounds, or MRI scans often prompt the need for a breast biopsy. Suspicious features, such as microcalcifications, irregular masses, or architectural distortions, can be indicative of breast cancer or other concerning conditions. Biopsies are performed to assess these abnormalities more definitively.
3. Nipple Discharge
Spontaneous nipple discharge, particularly if it is bloody, is a concerning symptom that may necessitate a breast biopsy. Biopsies help identify the cause of the discharge, which can range from benign conditions to cancerous growths within the breast ducts.
4. Breast Pain
While breast pain is a common concern, it can sometimes be associated with an underlying breast abnormality. In cases where breast pain is persistent, localized, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, a biopsy may be recommended to assess the source of the discomfort and rule out any serious conditions.
5. Changes in Breast Skin
Changes in the skin of the breast, such as redness, dimpling, or puckering, can be indicative of underlying issues, including cancer. A breast biopsy may be performed to investigate the skin changes and determine their cause, ensuring timely diagnosis and appropriate management.
6. Follow-Up for Prior Abnormalities
In some cases, patients may have a history of prior breast abnormalities that require ongoing monitoring. Breast biopsies are utilized as part of routine follow-up to ensure that any changes in the breast tissue are promptly identified and addressed.
Types of Breast Biopsies
There are several types of breast biopsies, each with its own approach and level of invasiveness. The choice of biopsy method depends on the characteristics of the breast abnormality and other factors, such as the patient's health and preferences. The main types of breast biopsies include:
1. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
FNA involves using a thin needle to extract a sample of cells or fluid from the breast lump. This method is typically used for cystic (fluid-filled) lumps or to remove a small amount of tissue for further analysis. It is a less invasive option and can often be performed in an outpatient setting.
2. Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
CNB is more invasive than FNA and is used to extract a small core of tissue from the suspicious area. This method provides a more substantial sample for examination and can be performed under local anesthesia. CNB is useful for diagnosing both benign and malignant breast abnormalities.
3. Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy (VAB)
VAB is a type of core needle biopsy that uses a vacuum-powered device to collect multiple tissue samples with a single insertion of the needle. This method is highly accurate and minimizes the need for multiple insertions.
4. Surgical Biopsy (Excisional or Incisional)
Surgical biopsies involve removing all or part of the suspicious tissue or lump for examination. Excisional biopsies remove the entire abnormality, while incisional biopsies remove only a portion. These procedures are typically performed in an operating room under general anesthesia.
The Breast Biopsy Procedure
The breast biopsy procedure is a vital diagnostic step to determine the nature of breast abnormalities, whether they are benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). This section will provide an in-depth understanding of what to expect during a breast biopsy procedure.
1. Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the biopsy, your healthcare provider will discuss the procedure with you and answer any questions you may have. They will also inquire about your medical history, including any allergies, medications you are taking, and your overall health. This is the time to inform your provider of any medications, such as blood thinners, that you are taking, as they may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped.
You will typically be asked to change into a hospital gown, and the healthcare team will ensure that you are comfortable and well-informed about the upcoming procedure.
2. Positioning
During the biopsy, you will be positioned in a way that allows the healthcare provider easy access to the breast abnormality. Depending on the type of biopsy and the location of the abnormality, you may be asked to sit, lie down, or stand.
3. Local Anesthesia
Most breast biopsies are performed under local anesthesia, which means that the breast tissue and the area surrounding the biopsy site will be numbed. This minimizes discomfort during the procedure. The healthcare provider will use a fine needle to inject the anesthesia, ensuring that you do not feel pain in the biopsy area.
4. Imaging Guidance
To accurately target the breast abnormality, the healthcare provider may use imaging guidance. The most common imaging methods for breast biopsies are ultrasound, mammography, or MRI. These techniques help the provider locate the exact area that needs to be biopsied.
5. Biopsy Procedure
The actual biopsy procedure will vary depending on the type of biopsy being performed. Here, we will focus on a core needle biopsy, which is one of the most common methods:
- A hollow, spring-loaded needle is inserted into the breast through a small incision in the skin. The healthcare provider uses the guidance of the imaging to ensure precise placement of the needle.
- Once the needle is in position, it is rapidly advanced into the breast to obtain a tissue sample. Several samples may be collected to ensure accuracy.
- As each sample is taken, you may feel some pressure or a brief sharp sensation, but you should not experience significant pain due to the local anesthesia.
- The samples are collected in a special chamber within the needle.
6. Wound Closure
After all the necessary tissue samples have been obtained, the healthcare provider will remove the needle and close the incision. This is typically done with a small adhesive bandage or, in some cases, with a few stitches.
7. Recovery
Following the biopsy, you will be monitored for a short period to ensure that you are recovering well. In most cases, you can go home on the same day as the procedure. You may experience some mild discomfort or bruising at the biopsy site, but this usually resolves within a few days.
Risks and Complications Associated with Breast Biopsies
While breast biopsies are a valuable diagnostic tool, like any medical procedure, they come with their own set of risks and potential complications. It's essential for patients to be aware of these risks and for healthcare providers to manage them effectively. In this section, we will delve into the potential risks and complications associated with breast biopsies.
1. Common Risks
1. Pain and Discomfort: It is common to experience some degree of pain or discomfort at the biopsy site after the procedure, especially in the first 24 to 48 hours. This discomfort can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
2. Bruising and Swelling: Bruising and swelling at the biopsy site are typical and may last for several days. These side effects are generally not a cause for concern but can be uncomfortable.
3. Infection: Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the biopsy site. Patients are typically given post-biopsy care instructions to reduce this risk, such as keeping the area clean and dry.
4. Bleeding: Some bleeding is expected after a biopsy, but it's usually minimal. In rare cases, excessive bleeding may occur, requiring medical attention.
2. Uncommon Risks
5. Scarring: Depending on the type of biopsy, there may be visible scarring. Minimally invasive techniques, such as core needle biopsies, tend to result in less scarring than surgical biopsies.
6. Allergic Reactions: Though rare, some individuals may have allergic reactions to medications or materials used during the biopsy, such as local anesthesia or adhesive bandages.
3. Serious Complications
7. Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: In very rare cases, the biopsy needle may damage nearby nerves or blood vessels, which can lead to persistent pain or other complications.
8. Inaccurate Results: While not a complication in the traditional sense, an inaccurate biopsy result is a significant concern. False negatives can lead to a delayed cancer diagnosis, while false positives can result in unnecessary anxiety and treatment.
9. Anxiety and Psychological Impact: Going through a breast biopsy can be emotionally taxing for some patients. The fear of a cancer diagnosis, along with the discomfort and waiting for results, can cause anxiety and stress.
4. Minimizing Risks and Complications
Healthcare providers take several precautions to minimize risks and complications during breast biopsies:
- Patient Selection: Ensuring that the patient is an appropriate candidate for the chosen biopsy type based on their specific case and medical history.
- Sterility: Maintaining a sterile environment during the procedure to reduce the risk of infection.
- Monitoring: Careful monitoring during and after the biopsy to address any complications promptly.
- Patient Education: Providing patients with clear pre- and post-biopsy instructions to reduce the likelihood of complications.
- Experience: Conducting biopsies by experienced and skilled healthcare professionals to minimize the risk of errors.
Breast Biopsy Cost and Considerations in UAE
1. Types of breast biopsies
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA): A thin needle is inserted into the breast to remove a small sample of cells. FNA is the least expensive type of breast biopsy, typically costing around AED 2,000.
- Core needle biopsy: A slightly larger needle is used to remove a larger sample of tissue from the breast. Core needle biopsy is more expensive than FNA, typically costing around AED 4,000.
- Surgical biopsy: A small incision is made in the breast and a piece of tissue is removed. Surgical biopsy is the most expensive type of breast biopsy, typically costing around AED 6,000 or more.
2. Hospital or clinic
The cost of a breast biopsy can also vary depending on the hospital or clinic where the biopsy is being done. Private hospitals and clinics are typically more expensive than public hospitals and clinics.
3. Insurance coverage
Most insurance plans in the UAE cover the cost of breast biopsies. However, it is important to check with your insurance company to see what your specific coverage is.
4. Considerations
There are a few things to consider when choosing a breast biopsy provider:
- Experience: The provider should have experience performing breast biopsies.
- Reputation: The provider should have a good reputation.
- Cost: The provider should be affordable.
- Location: The provider should be conveniently located.
5. Additional considerations
- Waiting times: Waiting times for breast biopsies can vary depending on the provider. It is important to ask about waiting times before scheduling your biopsy.
- Language: It is important to make sure that the provider can communicate with you in a language that you understand.
- Transportation: If you are not able to drive yourself to and from your biopsy appointment, make sure that the provider offers transportation assistance.
Understanding the Results of a Breast Biopsy
After undergoing a breast biopsy, waiting for the results can be an anxious and uncertain time for patients. The results of a breast biopsy provide critical information about the nature of a breast abnormality, whether it is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Understanding these results is essential for both patients and healthcare providers as they play a pivotal role in determining the subsequent steps in diagnosis and treatment. In this section, we will delve into the various possible outcomes of a breast biopsy and what they mean.
1. Benign Results
When the results of a breast biopsy indicate that the tissue sample is benign, it means that the examined tissue does not contain cancerous cells. This is reassuring news for the patient. Benign findings are common and may include conditions like fibroadenomas (non-cancerous breast lumps), cysts, or benign breast changes.
What it means:
- No immediate need for cancer treatment.
- Routine follow-up and monitoring may be recommended for some benign conditions.
- Patients can typically resume their regular breast health practices, such as breast self-exams and mammograms as advised by their healthcare provider.
2. Atypical or Unclear Results
In some cases, the biopsy results may fall into an "atypical" or "unclear" category. This means that the tissue sample shows unusual or uncertain features, making it challenging to definitively classify it as either benign or malignant. Further evaluation or follow-up may be recommended in these cases.
What it means:
- The medical team may recommend additional testing or imaging to gain more clarity about the abnormality.
- Regular follow-up appointments may be advised to monitor any changes over time.
- Atypical results do not definitively indicate cancer, but they require careful observation and sometimes additional procedures.
3. Malignant Results
A malignant result from a breast biopsy confirms the presence of cancerous cells in the tissue sample. This is often a distressing diagnosis, but it is a crucial step towards initiating treatment and improving the chances of a positive outcome. The type of breast cancer, its stage, and other characteristics revealed in the biopsy results will guide the development of a tailored treatment plan.
What it means:
- Immediate initiation of cancer treatment, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted therapies.
- A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals will work together to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
- Emotional support, education, and resources will be provided to help the patient navigate their cancer journey.
Future Benefits and Challenges of Breast Biopsies
Breast biopsies have come a long way in terms of accuracy and patient comfort, but as medical technology continues to advance, new benefits and challenges are on the horizon. In this section, we will explore some of the potential future benefits and challenges associated with breast biopsies.
Future Benefits
1. Enhanced Precision
With ongoing advancements in imaging technology and biopsy techniques, the precision of breast biopsies is likely to improve. This means that healthcare providers will be better equipped to distinguish between benign and malignant abnormalities, reducing the likelihood of false positives and unnecessary treatments.
2. Minimally Invasive Techniques
The future of breast biopsies may see a rise in minimally invasive techniques that cause less discomfort and scarring for patients. Procedures like VAB and stereotactic biopsies may become even less invasive, making them more accessible and less intimidating for patients.
3. Personalized Treatment Plans
Advancements in molecular diagnostics and genetic profiling may enable healthcare providers to develop highly personalized treatment plans based on the specific characteristics of a patient's breast cancer. This can lead to more effective and less invasive treatment options.
4. Screening and Early Detection
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into breast cancer screening may lead to earlier and more accurate detection of abnormalities. This could potentially reduce the need for invasive biopsies by detecting cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage.
5. Patient-Centered Care
Future breast biopsy practices may focus even more on patient-centered care, considering not only the medical aspects but also the emotional and psychological needs of patients. This holistic approach could lead to improved patient experiences and outcomes.
Future Challenges
1. Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment
As diagnostic techniques become more sensitive, there is a risk of overdiagnosis, where harmless abnormalities are identified as potential cancers. This can lead to overtreatment, causing unnecessary physical and emotional stress for patients.
2. Cost and Accessibility
While advanced biopsy techniques are promising, they can come with higher costs. Ensuring equitable access to these technologies for all patients, regardless of their economic status or geographic location, will be a critical challenge in the future.
3. Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
With the increasing use of AI and genetic profiling, concerns about data privacy and the ethical use of patient information will become more significant. Striking a balance between innovation and the protection of sensitive data is a challenge the healthcare industry will face.
4. Patient Anxiety
The psychological impact of undergoing a breast biopsy, even if minimally invasive, can be substantial. Reducing patient anxiety and ensuring they fully understand the process and potential outcomes will continue to be a challenge.
5. Rapid Technological Advancements
Keeping up with rapidly evolving technology and ensuring healthcare providers are trained and equipped to offer the latest and best practices in breast biopsies can be a challenge. Continuous education and investment in medical staff will be essential.
Conclusion
Breast biopsies are a vital component in the diagnosis of breast abnormalities, playing a significant role in determining whether a lump or mass is cancerous or not. Knowing the types of breast biopsies, reasons for conducting them, the procedure itself, and understanding the results can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health. If you or someone you know is facing a breast biopsy, remember that early detection and proper diagnosis are essential in the fight against breast cancer, and medical professionals are there to support you every step of the way.
Related Blogs
Why Choose Healthtrip for Medical Procedures in India? Cost & Quality
Explore the compelling reasons, from cost savings to expert care,

Your Guide to a Successful Healthtrip in Malaysia: Quality & Savings
Planning a healthtrip? Explore Malaysia for high-quality medical procedures and
Top Treatments at Chennai National Hospital: A Healthtrip Focus
Discover leading medical treatments available at Chennai National Hospital for

Healthtrip's Guide to IVF Clinics and Costs in UAE
Discover top IVF clinics in the UAE and understand treatment

Healthtrip's Guide to IVF Clinics and Costs in UAE
Discover top IVF clinics in the UAE and understand treatment

Revolutionizing Dialysis Treatment in the UAE
Mediclinic Al Twar Dialysis Center offers advanced dialysis treatment options










