
Anti-TPO Test and Thyroid Wellness
09 Sep, 2023
 Healthtrip
HealthtripIn the intricate web of human health, the thyroid gland plays a central role as a conductor of countless physiological processes. To understand and manage thyroid health, diagnostic tests are crucial, and one such test that shines a light on this vital gland is the Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody Test, commonly known as the Anti-TPO Test. In this enlightening blog, we will embark on a journey to uncover the significance of the Anti-TPO Test, its purpose, the conditions it helps diagnose, and what it means for your well-being.
1. The Thyroid: A Silent Hero in Health
Before we delve into the Anti-TPO Test, let's first grasp the importance of the thyroid gland. Nestled in your neck, this small, butterfly-shaped organ plays a mighty role in regulating metabolism, energy production, body temperature, and more.
Most popular procedures in India
2. The Anti-TPO Test: Decoding the Name
2.1 What Does Anti-TPO Stand For?
Anti-TPO stands for Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies. These antibodies target a key enzyme, thyroid peroxidase, essential for thyroid hormone production. The Anti-TPO Test measures the levels of these antibodies in your blood.
3. Unraveling the Significance of the Anti-TPO Test
3.1 Detecting Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders
Elevated levels of Anti-TPO antibodies are a telltale sign of autoimmune thyroid disorders, with Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease taking center stage. This test is instrumental in diagnosing these conditions accurately.
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
3.2 Predicting Thyroid Health Challenges
Anti-TPO antibodies can serve as early indicators of potential thyroid health issues, even if you haven't experienced noticeable symptoms. Early detection through the Anti-TPO Test empowers you to take proactive steps in managing your thyroid health.
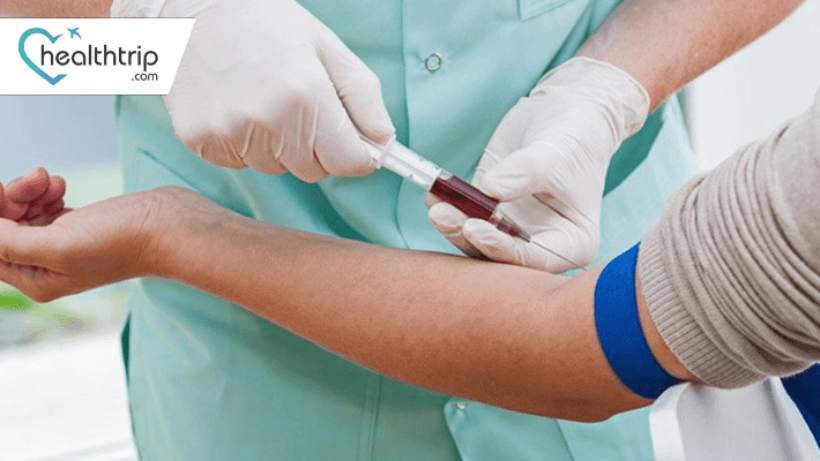
4. The Anti-TPO Test: A Simple Blood Draw
4.1 What to Expect
The Anti-TPO Test is a straightforward procedure that involves drawing a blood sample. A healthcare professional will typically collect this sample from a vein in your arm. The collected blood is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
5. Hashimoto's Thyroiditis vs. Graves' Disease
5.1 Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing inflammation and gradual destruction of thyroid tissue. Elevated Anti-TPO antibody levels are characteristic of this condition, leading to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
5.2 Graves' Disease
Graves' disease, on the other hand, involves the immune system stimulating the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones. While Anti-TPO antibodies are present in Graves' disease, they are often overshadowed by other antibodies, such as thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins.
6. Deciphering Anti-TPO Test Results
Interpreting the results of an Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody Test (Anti-TPO Test) is a crucial step in understanding thyroid health and diagnosing certain thyroid-related conditions. Let's explore how healthcare professionals decipher the results of this test:
6.1 Understanding Reference Ranges
Anti-TPO antibody levels are typically reported in international units per milliliter (IU/mL). To interpret these results, healthcare providers compare them to established reference ranges. The reference ranges help determine whether antibody levels fall within a normal or abnormal range.
6.2 Normal Anti-TPO Antibody Levels
- Normal Range: The normal reference range for Anti-TPO antibodies can vary slightly from one laboratory to another but is generally around 0 to 34 IU/mL.
- Interpretation: If your Anti-TPO antibody levels fall within this range, it suggests that there is no significant autoimmune attack on your thyroid gland. Your thyroid is functioning correctly, and there is no evidence of autoimmune thyroiditis.
6.3 Elevated Anti-TPO Antibody Levels
- Above Normal Range: Elevated Anti-TPO antibody levels are typically defined as values exceeding the upper limit of the reference range, often greater than 34 IU/mL.
- Interpretation: Elevated Anti-TPO antibody levels indicate the presence of an autoimmune response targeting the thyroid gland. This autoimmune response may lead to thyroid tissue damage and impact thyroid function.
6.4 Significance of Elevated Anti-TPO Antibodies
When Anti-TPO antibodies are elevated, healthcare providers consider several factors:
1. Symptoms: Elevated Anti-TPO antibodies may be associated with symptoms of thyroid dysfunction, such as fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, or changes in hair and skin.
2. Diagnosis: Elevated Anti-TPO antibodies can aid in diagnosing specific thyroid conditions, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease that leads to hypothyroidism. In some cases, elevated Anti-TPO antibodies may also be present in Graves' disease, an autoimmune condition causing hyperthyroidism.
3. Risk Assessment: Even in the absence of symptoms, elevated Anti-TPO antibodies can indicate an increased risk of developing thyroid disorders in the future. Regular monitoring and proactive management may be recommended to address potential thyroid health challenges.
6.5 Follow-Up and Additional Testing
When Anti-TPO antibody levels are elevated, healthcare providers may recommend additional tests to assess thyroid function, such as measuring thyroid hormones (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). These tests help determine whether the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism).
7. Management and Treatment
Upon receiving the results of an Anti-TPO Test, the next crucial step is determining the appropriate management and treatment plan based on the diagnosis. Let's explore how healthcare providers approach the management and treatment of thyroid conditions associated with elevated Anti-TPO antibodies, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease:
7.1 Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Treatment Objective: The primary goal in managing Hashimoto's thyroiditis is to restore normal thyroid hormone levels, alleviate symptoms of hypothyroidism, and slow the progression of the autoimmune attack on the thyroid gland.
1. Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: The cornerstone of treatment for Hashimoto's is thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Patients are typically prescribed synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine (Synthroid). These medications replace the deficient thyroid hormones (T4 and T3) and help regulate metabolism.
2. Regular Monitoring: Patients with Hashimoto's require ongoing monitoring of thyroid function through blood tests. The dosage of thyroid hormone replacement medication may need adjustment over time to maintain optimal hormone levels.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can complement medical treatment. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management practices, all of which can contribute to overall well-being.
7.2 Graves' Disease
Treatment Objective: In the case of Graves' disease, the aim is to normalize thyroid hormone levels and manage the symptoms of hyperthyroidism while addressing the autoimmune aspect of the condition.
1. Medications: Depending on the severity of symptoms, healthcare providers may prescribe antithyroid medications like methimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU). These drugs inhibit the excessive production of thyroid hormones.
2. Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety while waiting for antithyroid medications to take effect.
3. Radioactive Iodine Therapy: In some cases, radioactive iodine therapy may be recommended. This treatment damages the overactive thyroid cells, effectively reducing hormone production. It often leads to hypothyroidism, which can be managed with thyroid hormone replacement.
4. Surgery: Thyroidectomy, the surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland is reserved for cases where medications and radioactive iodine therapy are ineffective or inappropriate.
7.3 Individualized Care
Thyroid conditions are highly individualized, and treatment plans are tailored to each patient's specific needs. Close collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is essential to achieve optimal outcomes.
Regular Follow-Up: Regardless of the thyroid condition being treated, regular follow-up appointments and ongoing monitoring of thyroid function are essential. These visits allow for adjustments to medication dosages and ensure that the thyroid remains stable.
Patient Education: Patients should be actively involved in their care and educated about their condition. Understanding the importance of medication adherence, recognizing potential side effects, and knowing when to seek medical attention are vital components of self-management.
In conclusion, the management and treatment of thyroid conditions associated with elevated Anti-TPO antibodies require a multidisciplinary approach. With appropriate medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing monitoring, individuals with thyroid disorders can achieve improved thyroid health, symptom relief, and an enhanced quality of life. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of each patient.
Related Blogs
Thyroid's Silent Messenger: The TPO Test Explained
Your thyroid gland, though small in size, plays a significant
Thyroglossal Cyst: Can Surgery Be an Option?
Overview A thyroglossal duct cyst develops when the thyroid gland in
Early Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer: Know It All
Overview With the increasing number of new thyroid cancer cases every










