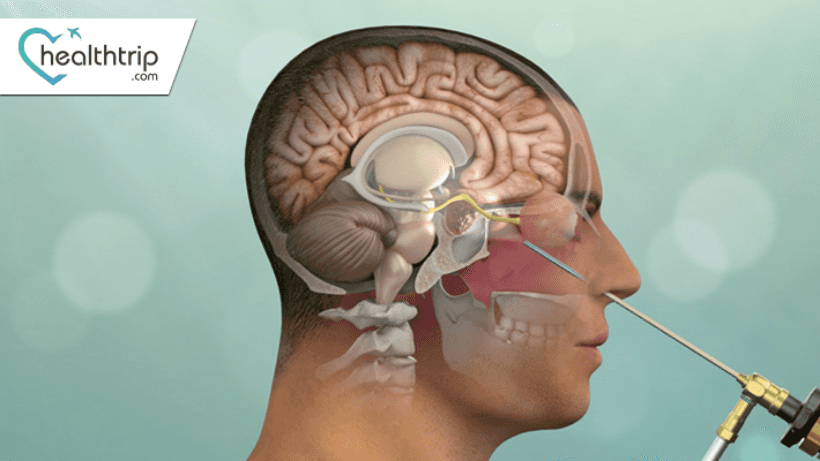
Pituitary Tumors : Types, Symptoms, Treatments
29 Sep, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamWelcome to the exploration of pituitary tumors—mysterious anomalies nestled in the brain's command center. Join us on this journey as we unravel the definition, types, symptoms, causes, and roadmap to treatment. We'll navigate the risk factors, complications, and strategies for prevention, capping it off with a glimpse into the outlook and key takeaways.
What are Pituitary tumors ?
Most popular procedures in India
Pituitary tumors are like unexpected guests in the brain's control center, the pituitary gland. This tiny but crucial gland manages the hormones that keep our body working smoothly. Sometimes, though, certain cells decide to misbehave, growing into what we call pituitary tumors.
Types of Pituitary Tumors
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
1. Non-functioning Pituitary Tumors:
These are the silent intruders that, unlike their hormone-producing counterparts, don't mess with our body's chemical balance. However, their presence can lead to issues by pressing on nearby structures, causing symptoms like headaches or vision problems.
2. Functioning Pituitary Tumors:
In contrast, these tumors are the overachievers of the pituitary world, producing excess hormones. Let's break down this category further:
- Prolactinomas: These tumors hyperactively churn out prolactin, a hormone responsible for breast milk production. This overproduction can lead to irregular periods in women and, in men, cause issues like erectile dysfunction.
Prolactinomas are the most common type of pituitary tumor, accounting for about more than one-fourth of all cases
- Growth Hormone-secreting Tumors: As the name suggests, these tumors overdrive the production of growth hormone, triggering gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults. Unusual growth of hands, feet, and facial features are telltale signs.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)-secreting Tumors: The culprit here is an excess of ACTH, which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce more cortisol. This can result in Cushing's disease, characterized by weight gain, fragile skin, and muscle weakness.
- Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)-secreting Tumors: This variety cranks up the production of TSH, causing the thyroid gland to go into overdrive. The result is hyperthyroidism, bringing symptoms like weight loss, nervousness, and rapid heartbeats.
Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring treatments to the specific challenges posed by each category of pituitary tumor.
Symptoms and Signs of of Pituitary Tumors
1. Vision Problems:
- Visual Field Loss: Tumors can exert pressure on the optic nerve, leading to a gradual loss of peripheral vision.
- Double Vision: Some patients may experience seeing double due to the disruption of normal eye movements caused by the tumor's impact.
2. Headaches:
- Intensity and Frequency: Persistent and severe headaches are common, often worsening in intensity over time.
- Morning Headaches: Headaches in the morning may be indicative of increased pressure within the skull during sleep.
3. Hormonal Changes:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Women may notice changes in their menstrual periods due to hormonal imbalances caused by certain pituitary tumors, particularly prolactinomas.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Men and women might experience a decrease in libido or sexual function due to disruptions in hormone levels.
4. Fatigue:
- Chronic Fatigue: A pervasive sense of tiredness and lack of energy is a frequent complaint.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness can be attributed to hormonal imbalances or, in the case of ACTH-secreting tumors, excess cortisol affecting muscle strength.
5. Nausea and Vomiting:
- Pressure on Surrounding Structures: Tumors can press on adjacent areas, triggering nausea and vomiting.
- Hormonal Influence: Changes in hormone levels, particularly with certain functioning tumors, may induce feelings of nausea.
Understanding and recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention, improving the prognosis for individuals with pituitary tumors.
Causes of Pituitary Tumors
1. Genetic Factors:
- Inherited Mutations: Certain genetic conditions, like multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) or Carney complex, can increase the risk of developing pituitary tumors.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of pituitary tumors may have a higher likelihood of inheriting genetic predispositions.
2. Sporadic Mutations:
- Random Genetic Changes: In many cases, pituitary tumors occur sporadically, with no clear genetic link. Random mutations in the DNA of pituitary cells can trigger uncontrolled growth.
3. Other Medical Conditions:
- Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation, especially to the head and neck region, increases the risk of pituitary tumors.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions causing imbalances in sex hormones, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may contribute to the development of certain pituitary tumors.
Understanding the diverse factors that can contribute to the genesis of pituitary tumors is crucial for both preventive measures and early intervention. Regular screenings and genetic counseling can play pivotal roles in identifying and managing potential risk factors.
How are pituitary tumors diagnosed?
1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- Detailed Imaging: MRI scans provide detailed images of the pituitary gland, helping identify the size, location, and characteristics of the tumor.
- Visualizing Surrounding Structures: This diagnostic tool is crucial for assessing whether the tumor is pressing on nearby structures, such as the optic nerve.
2. Blood Tests:
- Hormone Levels: Blood tests can detect abnormal hormone levels, indicating the presence of a functioning pituitary tumor.
- Tumor Markers: Specific markers in the blood can help diagnose certain types of pituitary tumors, such as elevated prolactin levels in prolactinomas.
3. Vision Tests:
- Visual Field Examination: Evaluating the patient's peripheral vision helps assess the impact of the tumor on the optic nerve.
- Eye Movement Tests: These tests can reveal abnormalities caused by pressure on the nerves controlling eye movements.
4. Hormone Tests:
- Stimulation and Suppression Tests: These tests involve administering substances to provoke or suppress hormone release, aiding in the diagnosis of functioning pituitary tumors.
- Comprehensive Hormone Panels: Analyzing a range of hormones helps identify specific hormonal imbalances associated with different types of tumors.
Treatments of of Pituitary Tumors
1. Medications:
- Prolactin Inhibitors: Used for prolactinomas to normalize prolactin levels and restore reproductive function.
- Somatostatin Analogs: Control excess growth hormone production in growth hormone-secreting tumors.
- Corticosteroids: Manage symptoms associated with ACTH-secreting tumors by reducing cortisol production.
2. Surgery:
- Transsphenoidal Surgery: A minimally invasive approach where the tumor is removed through the nasal cavity or upper lip, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
- Craniotomy: In more complex cases, an open-skull surgery may be necessary to access and remove the tumor.
3. Radiation Therapy:
- Conventional Radiation: External beam radiation targets the tumor with high-energy rays.
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: Precise radiation delivered in a single session, often suitable for small tumors or those in challenging locations.
Treatment approaches are tailored to the type and size of the tumor, its impact on surrounding structures, and the overall health of the patient. A multidisciplinary approach involving endocrinologists, neurosurgeons, and radiation oncologists is typically employed to optimize outcomes.
How can we help with the treatment?
If you're on the lookout for treatment in India, let Healthtrip be your compass. We will serve as your guide throughout your medical treatment. We'll be by your side, in person, even before your medical journey commences. The following will be provided to you:
- Connect withrenowned doctors from a network spanning 35+ countries and access the world's largest health travel platform.
- Collaboration with 335+ top hospitals , including Fortis and Medanta.
- Comprehensive treatments from Neuro to Cardiac to Transplants, Aesthetics, and Wellness.
- Post-treatment care and assistance.
- Teleconsultations at $1/minute with leading surgeons.
- Trusted by 44,000+ patients for appointments, travel, visa, and forex assistance.
- Access top treatments and packages, such as Angiograms and many more.
- Gain insights from genuine patient experiences and testimonials.
- Stay updated with our medical blog.
- 24/7 unwavering support, from hospital formalities to travel arrangements or emergencies.
- Pre-scheduled specialist appointments.
- Prompt emergency assistance, ensuring safety.
Our patient success stories
See more inspiring testimonials of Healthtrip
Risk Factors of Pituitary Tumors
1. Age:
- Incidence Increases with Age: Pituitary tumors are more commonly diagnosed in adults, with the risk rising as individuals get older.
- Occurrence in Children: While rare, these tumors can also affect children and adolescents.
2. Gender:
- Gender Disparities: Certain types of pituitary tumors, like prolactinomas, are more prevalent in specific genders. For instance, prolactinomas are more common in women.
3. Family History:
- Hereditary Predisposition: A family history of pituitary tumors can elevate the risk, suggesting a genetic component.
- Underlying Genetic Syndromes: Inherited conditions, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1), can run in families and increase susceptibility.
4. Inherited Conditions:
- Genetic Syndromes: Conditions like MEN1, Carney complex, and McCune-Albright syndrome increase the likelihood of developing pituitary tumors.
- Genetic Testing: Individuals with known genetic predispositions may undergo genetic testing for early detection.
Complications of Pituitary Tumors
1. Vision Loss:
- Optic Nerve Compression: Tumors pressing on the optic nerve can lead to gradual vision loss if not addressed promptly.
- Visual Field Defects: Peripheral vision may be compromised, impacting daily activities.
2. Hormonal Imbalances:
- Endocrine Dysfunction: Pituitary tumors, especially functioning ones, can disrupt hormone balance, leading to a cascade of systemic effects.
- Metabolic Consequences: Conditions like Cushing's syndrome can result in metabolic disturbances, including weight gain and diabetes.
3. Neurological Issues:
- Headaches and Migraines: Persistent headaches are a common complication, impacting quality of life.
- Neurological Deficits: In severe cases, larger tumors may cause neurological deficits, affecting coordination and cognitive function.
Prevention
1. Regular Health Check-ups:
- Early Detection: Routine health check-ups, including comprehensive physical exams, can aid in the early detection of symptoms or signs of pituitary tumors.
- Screening for Hormonal Imbalances: Periodic screenings for hormonal imbalances, especially for those at higher risk, can facilitate early intervention.
2. Genetic Counseling:
- Identifying Genetic Predisposition: For individuals with a family history or known genetic syndromes, genetic counseling can provide insights into the risk and guide preventive measures.
- Informed Decision-Making: Genetic counseling empowers individuals to make informed decisions about monitoring and potential interventions.
Managing Risk Factors:
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can contribute to overall well-being.
- Monitoring Hormonal Health: Individuals with known risk factors can benefit from regular hormonal screenings to detect imbalances early on.
Understanding and addressing these risk factors, complications, and preventive measures are integral components in the holistic management of pituitary tumors. Regular collaboration with healthcare professionals is crucial for tailored strategies based on individual health profiles.
Takeaways
- Pituitary tumors vary, with non-functioning and hormone-secreting types like prolactinomas.
- Symptoms include vision problems, headaches, hormonal changes, fatigue, and nausea.
- Genetic factors, sporadic mutations, and other medical conditions can contribute to pituitary tumors.
- Diagnosis involves MRI, blood, vision, and hormone tests for a thorough understanding.
- Treatment includes medications, surgery, and radiation therapy, offering a comprehensive approach.
Related Blogs

Understanding Amblyopia
Get the facts about amblyopia, also known as lazy eye,
Urinary Bladder Carcinoma Radiation Therapy and Palliative Care
Radiation therapy can provide palliative care for urinary bladder carcinoma
Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer in Elderly Patients
Radiation therapy is a suitable treatment option for elderly patients
Bladder Cancer Treatment with Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy
Learn about the combination of radiation therapy and immunotherapy for
Urinary Bladder Carcinoma Radiation Therapy and Quality of Life
Radiation therapy can improve quality of life for urinary bladder
Bladder Cancer Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy Side Effects
Learn about the side effects of combining radiation therapy and










