Fallopian Tube Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
11 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamWhat are fallopian tubes?
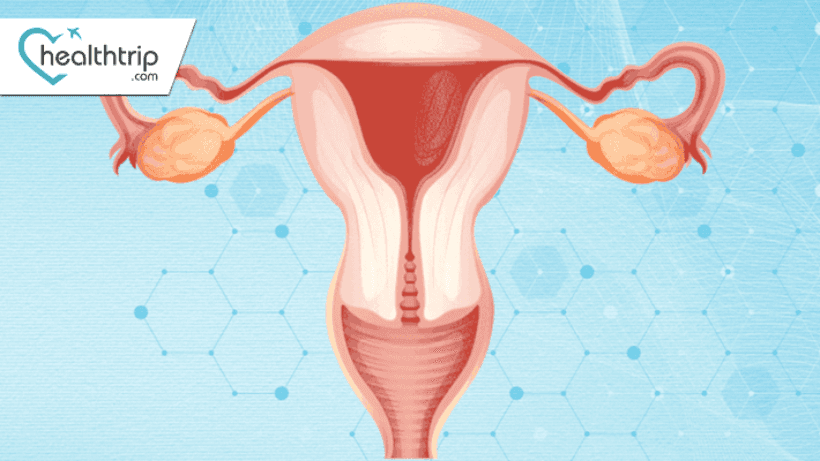
The fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, are a pair of narrow, tube-like structures in the female reproductive system. They extend from the ovaries to the uterus, and their primary function is to transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. During ovulation, an egg is released from an ovary, and the fallopian tubes provide a pathway for the egg to travel toward the uterus. If the egg is fertilized by sperm during this journey, fertilization typically occurs within the fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg then continues its journey to the uterus for implantation and pregnancy.
Most popular procedures in India
The fallopian tubes are essential for the reproductive process, playing a crucial role in the fertilization of the egg and early stages of embryonic development. Issues with the fallopian tubes, such as blockages or the development of cancer, can impact fertility and reproductive health.
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
Fallopian tube cancer
Fallopian tube cancer refers to the development of malignant cells within the fallopian tubes, which are part of the female reproductive system. These slender tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus and play a crucial role in transporting eggs. The cancer can be categorized as primary, originating within the fallopian tubes, or secondary, spreading from other areas.
what are the symptoms and signs of fallopian tube cancer ?
Lets look at the fallopian tube cancer symptoms and signs
- Pelvic Pain:
- Persistent or worsening pain in the pelvic region, potentially indicating the presence of a tumor in the fallopian tubes.
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding:
- Unusual bleeding not associated with regular menstruation, such as spotting between periods or postmenopausal bleeding.
- Changes in Menstruation:
- Irregularities in menstrual cycles, including changes in flow, duration, or frequency.
- Abdominal Bloating:
- Persistent feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdominal area, sometimes accompanied by discomfort.
- Other Possible Symptoms:
- Back pain
- Fatigue
- Changes in urinary habits
- Unexplained weight loss
Causes of fallopian tube cancer:
- Genetic Factors:
- Presence of specific gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, increasing susceptibility to fallopian tube cancer.
- Family History:
- Individuals with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer may be at a higher risk.
- Hormonal Factors:
- Hormonal imbalances or long-term hormonal replacement therapy may contribute to the development of fallopian tube cancer.
- Other Potential Causes:
- Environmental factors or exposure to toxins.
- Inflammation or infection of the fallopian tubes may be associated with increased risk.
Diagnosis of fallopian tube cancer
1. Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves create images to detect abnormalities in the pelvic region.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): X-rays produce cross-sectional images, aiding in identifying tumor size and spread.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Detailed images using magnetic fields and radio waves, helpful for assessing soft tissue involvement.
2. Biopsy:
- Removal of a small tissue sample for microscopic examination to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Types include fine-needle aspiration or surgical biopsy.
3. Blood Tests (CA-125):
- Measurement of the CA-125 protein levels in the blood.
- Elevated levels may indicate the presence of certain cancers, including fallopian tube cancer.
4. Surgical Exploration:
- Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive procedure using a thin, lighted tube with a camera (laparoscope) to examine the pelvic organs.
- Exploratory Laparotomy: Surgical exploration involving a larger incision for a more comprehensive examination of the abdominal cavity.
Treatment of Fallopian Tube Cancer
Fallopian tube cancer, though rare, presents unique challenges in terms of treatment. A thorough understanding of the available treatment options and their implications is crucial. This comprehensive guide dives deeper into the various aspects of managing fallopian tube cancer.
1. Surgical Intervention: The Cornerstone of Treatment
Surgery is the primary and often initial step in treating fallopian tube cancer. The surgical approach may vary based on the extent of cancer and the patient's specific circumstances:
- Salpingectomy: A salpingectomy involves the removal of the affected fallopian tube(s). It is the standard procedure for early-stage fallopian tube cancer. Surgeons aim to excise the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal.
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy: In certain cases, particularly for postmenopausal patients or when cancer has spread beyond the fallopian tubes, a total abdominal hysterectomy may be recommended. This procedure entails the removal of the uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes.
2. Assessing Spread and Extent: Lymph Node Dissection and Omentectomy
During surgery, additional steps may be taken to assess the extent of cancer spread and ensure thorough treatment:
- Lymph Node Dissection: The removal and examination of nearby lymph nodes help determine whether cancer has spread beyond the fallopian tubes. If cancer is detected in the lymph nodes, it may influence further treatment decisions.
- Omentectomy: In cases where there is a concern about cancer spread to the omentum (a fatty tissue apron covering abdominal organs), an omentectomy may be performed. This procedure aims to eliminate potential cancer cells in the omentum.
3. Targeting Residual Cancer Cells: Chemotherapy
Following surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy is a standard treatment approach for fallopian tube cancer. Chemotherapy involves the administration of drugs to destroy any remaining cancer cells:
- Chemotherapy Drugs: The choice of chemotherapy drugs depends on the specific type and stage of fallopian tube cancer. Platinum-based drugs like cisplatin or carboplatin are commonly used in combination with other drugs such as paclitaxel. These medications are typically administered intravenously or orally.
- Personalized Treatment: Oncologists tailor chemotherapy regimens to each patient, considering factors like age, overall health, and the specific characteristics of the cancer. Personalization ensures the most effective and tolerable treatment.
4. Radiation Therapy: An Option in Specific Cases
Radiation therapy is not frequently employed in the treatment of fallopian tube cancer but may be considered in certain scenarios:
- External Beam Radiation: External beam radiation therapy involves directing high-energy X-rays at the tumor site from outside the body. This precise method can be used to target specific areas, such as residual cancer cells after surgery.
- Brachytherapy: In brachytherapy, a radiation source is placed directly inside or near the tumor. It is used less frequently in fallopian tube cancer but may be an option in select cases.
5. Exploring Targeted Therapies
While targeted therapies are not the primary treatment for fallopian tube cancer, ongoing research is exploring their potential:
- Targeted Approaches: Targeted therapies focus on specific molecules or pathways that play a role in cancer growth. By interfering with these specific targets, these therapies aim to inhibit cancer cell proliferation.
- Clinical Trials: Many clinical trials are investigating the effectiveness of targeted therapies in various cancer types, including fallopian tube cancer. Patients with advanced or refractory disease may consider participating in these trials to access cutting-edge treatments.
6. Clinical Trials: Pioneering Treatments
Clinical trials are invaluable in advancing our understanding of fallopian tube cancer and developing innovative treatment strategies:
- Innovative Treatments: Clinical trials offer patients access to promising treatments that are not yet widely available. These trials assess the safety and efficacy of new therapies, combinations, and approaches.
- Patient Participation: Patients with advanced or recurrent fallopian tube cancer can contribute to medical progress by participating in clinical trials. Discussing trial options with your healthcare team is essential to determine if you are a suitable candidate.
7. Enhancing Quality of Life: Supportive Care
Supportive care is an integral component of fallopian tube cancer treatment, addressing both physical and emotional aspects:
- Pain Management: Managing pain is essential to improve the patient's comfort and well-being. Various pain management strategies, including medications and non-pharmacological approaches, can be employed.
- Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition is crucial during cancer treatment. Registered dietitians can provide guidance on maintaining a balanced diet and addressing any dietary challenges that may arise.
- Emotional Assistance: Coping with a cancer diagnosis and treatment can be emotionally challenging. Psychosocial support, counseling, and support groups can help patients and their families navigate these emotional hurdles.
In summary, the treatment of fallopian tube cancer is a complex and evolving field. Collaborating closely with healthcare experts, staying informed about available treatment options, and actively participating in treatment decisions are key factors in achieving the best possible outcomes. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress, manage side effects, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Risk factors for fallopian tube cancer:
1. Family history of ovarian or breast cancer:
- Individuals with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer have a higher risk of developing fallopian tube cancer. The presence of these cancers in close relatives, such as a mother, sister, or daughter, may suggest a genetic predisposition.
- Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly increase the risk of fallopian tube cancer. Genetic testing can identify these mutations, helping individuals make informed decisions about preventive measures and screening.
- While fallopian tube cancer can occur at any age, the risk increases with age, especially in women over 50. Regular health check-ups become crucial as individuals enter this age group.
- Certain reproductive factors may influence the risk of fallopian tube cancer. For example, women who have never given birth or have a history of infertility may face a slightly elevated risk.
Complications of fallopian tube cancer:
1. Spread to nearby organs:
In advanced stages, fallopian tube cancer may spread to nearby organs such as the ovaries, uterus, or other pelvic structures. This can complicate treatment and affect overall prognosis.
2. Treatment-Related Complications:
Surgical procedures, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may have associated complications. Surgical complications can include bleeding or infection, while chemotherapy and radiation can cause side effects like fatigue, nausea, and weakened immune function.
3. Recurrence:
Despite successful treatment, there's always a risk of cancer recurrence. Regular follow-up appointments and surveillance are essential to detect any signs of recurrence early.
Prevention of fallopian tube cancer:
1. Risk-Reduction Surgeries (Prophylactic Oophorectomy):
- In individuals at high risk due to family history or genetic mutations, the removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) may be recommended as a preventive measure. This can significantly reduce the risk of developing fallopian tube cancer.
- Genetic counseling can help individuals understand their risk based on family history and guide them in making decisions about genetic testing. Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations can provide valuable information for preventive strategies.
- For individuals with a history of fallopian tube cancer, the use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be approached cautiously. It's important to discuss the potential risks and benefits with healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding HRT.
Outlook/Prognosis:
1. Stage at Diagnosis:
- Early-stage diagnosis generally correlates with better outcomes.
- Staging determines the extent of cancer spread.
- Positive response to surgery, chemotherapy, and other therapies improves prognosis.
- Vary based on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer.
- Potential for treatment-related side effects, including fertility issues and hormonal imbalances.
Related Blogs

How Healthtrip Ensures Quality & Safety in Cancer Treatment Procedures
Detailed guide on cancer treatment, featuring doctors, hospitals, risks, recovery,
End-to-End Logistics for Cancer Treatment with Healthtrip's Support
Detailed guide on cancer treatment, featuring doctors, hospitals, risks, recovery,
Healthtrip's Care Coordinators: Your Support During Cancer Treatment
Detailed guide on cancer treatment, featuring doctors, hospitals, risks, recovery,
Healthtrip's Care Coordinators: Your Support During Cancer Treatment
Detailed guide on cancer treatment, featuring doctors, hospitals, risks, recovery,

Top 5 Indian Hospitals for Cancer Treatment
Detailed guide on cancer treatment, featuring doctors, hospitals, risks, recovery,
Post-Cancer Treatment Diet and Lifestyle Tips
Detailed guide on cancer treatment, featuring doctors, hospitals, risks, recovery,










