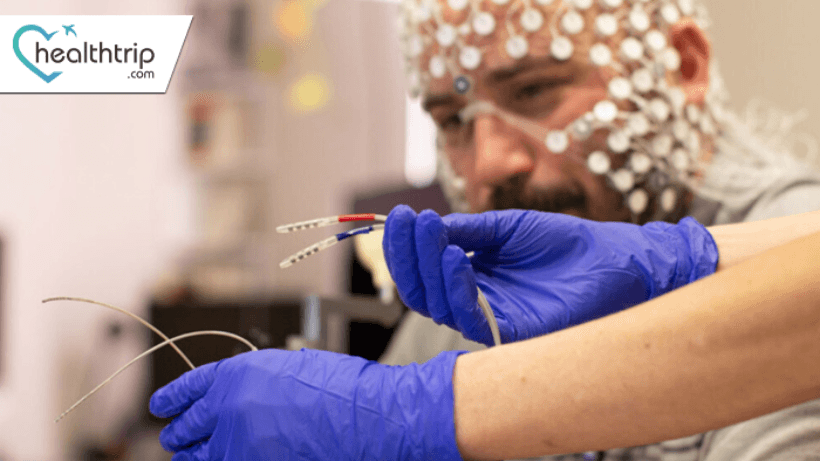

DBS for Depression: Illuminating Advances in Mental Health Innovation
16 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamDepression, a common mental health disorder, is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in daily activities. - It affects millions worldwide, cutting across age, gender, and socio-economic boundaries.
The Crucial Need for Innovation -
Most popular procedures in India
Existing treatments for depression, while beneficial for many, have limitations. - Introduction of innovative approaches is essential to address the diverse and complex nature of mental health conditions.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) -
DBS emerges as a promising frontier in mental health innovation. - Unlike traditional methods, DBS involves targeted stimulation of specific brain areas to alleviate symptoms.
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
Depression
A. Decoding Depression -
Depression involves a range of symptoms, such as persistent sadness, changes in sleep and appetite, and a diminished ability to experience pleasure. - It extends beyond a transient low mood, often becoming a chronic condition.
B. The Widespread Impact -
Depression's prevalence is staggering, affecting individuals globally. - Its repercussions extend beyond the individual to impact relationships, work, and overall societal well-being.
C. Gaps in Current Treatments -
Existing treatments, including medications and therapy, may not provide effective relief for everyone. - Accessibility and stigma further impede the reach and success of conventional treatments.
Explanation of DBS and its Origins
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure that involves the implantation of a medical device, often referred to as a "brain pacemaker," into specific areas of the brain. The origins of DBS can be traced back to the late 1980s and early 1990s when the technique was initially explored as a treatment for movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease. The pioneering work of researchers like Alim Louis Benabid laid the foundation for the development of DBS as a therapeutic option for various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The procedure typically involves the implantation of thin electrodes into specific brain regions. These electrodes are connected to a pulse generator, a device similar to a cardiac pacemaker, which is usually implanted under the skin near the collarbone. The pulse generator delivers electrical impulses to modulate the activity of targeted brain areas.
B. Mechanism of Action in the Context of Depression
In the context of Depression, DBS is primarily targeted at brain regions associated with mood regulation. The exact mechanisms of how DBS alleviates depressive symptoms are not fully understood, but it is believed to modulate the neural circuits involved in mood regulation.
- Neurotransmitter Modulation: DBS is thought to influence the release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play crucial roles in mood regulation. By modulating the activity of specific brain regions, DBS may impact the balance of these neurotransmitters.
- Neuroplasticity: The electrical stimulation induced by DBS may trigger neuroplastic changes in the brain. This could involve the formation of new neural connections or the alteration of existing ones, contributing to improvements in mood.
- Network Effects: Depression is associated with dysfunctional neural networks. DBS may help normalize these networks by regulating the activity of interconnected brain regions, leading to a more balanced and resilient mood state.
C. Research and Clinical Trials Supporting the Use of DBS for Depression
Numerous research studies and clinical trials have been conducted to investigate the efficacy of DBS for Depression. While results can vary, some key findings include:
- Early Studies: Initial studies focused on small patient samples and showed promising results, prompting further exploration of DBS as a potential treatment for severe, treatment-resistant depression.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs): Rigorous RCTs have been conducted to assess the effectiveness of DBS compared to sham (placebo) stimulation. These trials provide more robust evidence of the therapeutic potential of DBS for Depression.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Some studies have followed patients over extended periods, demonstrating that the benefits of DBS can be sustained over time, making it a viable option for long-term management of depression.
- Patient Stratification: Ongoing research aims to identify patient characteristics that predict a positive response to DBS, allowing for more personalized and targeted treatment approaches.
Despite these positive findings, challenges and nuances exist, including variations in response rates, potential side effects, and the need for further research to optimize stimulation parameters and patient selection. Ongoing investigations continue to refine our understanding of the role of DBS in the treatment landscape for Depression.
A. Contrast DBS with Traditional Antidepressant Medications
- Mechanism of Action:
- DBS: Involves the direct modulation of neural circuits through electrical stimulation.
- Antidepressant Medications: Typically act by altering the balance of neurotransmitters (e.g., serotonin, norepinephrine) in the brain.
- Speed of Onset:
- DBS: Effects may take time to manifest, with gradual improvements observed over weeks to months.
- Antidepressant Medications: Some medications can take weeks to months to reach their full therapeutic effect.
- Response Rate:
- DBS: Response rates can vary, and not all individuals respond positively.
- Antidepressant Medications: Response rates vary among individuals, and not everyone responds to the first medication tried.
- Treatment Resistance:
- DBS: Considered for individuals with treatment-resistant depression who haven't responded to multiple medication trials.
- Antidepressant Medications: May be less effective in cases of treatment-resistant depression.
B. Comparison with Psychotherapy and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- Therapeutic Approach:
- DBS: Involves direct neurostimulation to modulate brain activity.
- Psychotherapy: Focuses on verbal communication and behavioral interventions.
- ECT: Induces controlled seizures to impact neurotransmitter release and alleviate severe depression.
- Treatment Duration:
- DBS: Generally requires continuous stimulation for ongoing benefits.
- Psychotherapy: Involves regular sessions over an extended period.
- ECT: Usually administered in a series of sessions, with maintenance treatments as needed.
- Side Effects:
- DBS: Can have side effects related to the surgical procedure and stimulation, such as mood changes or cognitive effects.
- Psychotherapy: Generally considered safe, with minimal side effects.
- ECT: Can cause short-term memory loss and cognitive side effects.
- Indications:
- DBS: Primarily considered for severe, treatment-resistant depression.
- Psychotherapy: Applicable to a broad range of depressive disorders.
- ECT: Reserved for severe cases, often when other treatments haven't been effective.
C. Advantages and Disadvantages of DBS
Advantages:
- Treatment-Resistant Cases: Effective for individuals who have not responded to traditional treatments, providing a potential option for those with severe depression.
- Long-Term Management: Offers the possibility of sustained benefits over the long term, reducing the need for frequent adjustments or changes in treatment.
- Targeted Intervention: Allows for precise targeting of specific brain regions, providing a more localized and personalized approach compared to systemic medications.
Disadvantages:
- Surgical Risks: Involves a surgical procedure, which carries inherent risks such as infection, bleeding, or complications related to the implantation of the device.
- Cost and Accessibility: The procedure and associated devices can be costly, and availability may be limited, impacting accessibility for some individuals.
- Variable Response: Response rates can vary, and not all individuals experience significant improvement, necessitating careful patient selection.
- Ethical Considerations: Involves ethical considerations related to the invasive nature of the procedure, potential side effects, and the long-term impact on patients' well-being.
In conclusion, Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) emerges as a promising frontier in treating depression, offering a targeted approach for individuals resistant to conventional therapies. As we weigh its advantages against potential drawbacks and compare it with traditional treatments, the nuanced landscape of mental health interventions comes into focus. The hope for the future of mental health treatments is not confined to DBS alone but extends to a broader horizon of technological and scientific innovations.
This calls for sustained research, collaboration, and a collective commitment to advance mental health solutions. As we stand at the intersection of neuroscience and technology, the imperative is clear – to push boundaries, unravel complexities, and pave the way for a future where mental well-being is not only understood but profoundly enhanced.
Related Blogs
Advances in Lymphoma Treatment in the UK
Navigating lymphoma treatment options can be overwhelming, especially for patients

Targeted Therapy for Breast Cancer: Personalized Treatment Plans at Bumrungrad
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting

Innovative Breast Cancer Surgery at Bumrungrad
Breast cancer remains one of the most common cancers affecting

Personalized Cancer Treatment Plans in UAE
Cancer treatment has evolved significantly over the past decade, moving

3D Printing Technology for Customized Cancer Treatment Plans in UAE
Cancer treatment has advanced significantly over the past few decades,

Precision Medicine in Liver Transplants: Genetic Matching in UAE Hospitals
Liver transplantation is a critical and life-saving procedure for patients










