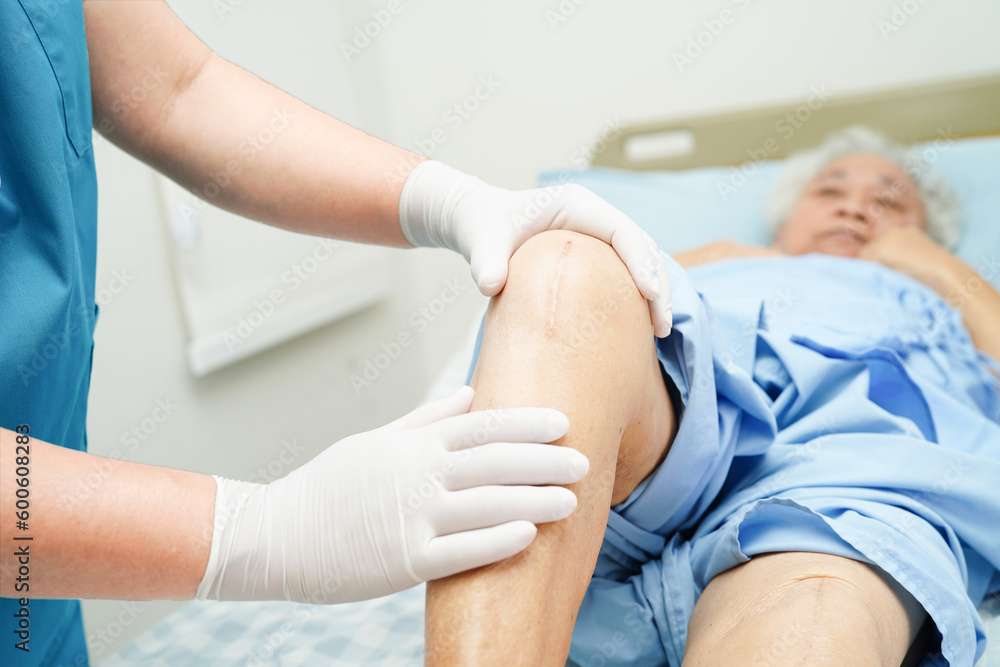
A Guide to knee Replacements in the UK
02 Aug, 2024
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamKnee replacement surgery, or knee arthroplasty, is a common and effective procedure aimed at relieving pain and restoring function in severely damaged knee joints. This guide will cover various aspects of knee replacements, including why the UK is an excellent choice for this surgery, the types of knee replacements, the procedure, pre- and post-operative care, and how to choose the right surgeon.
Most popular procedures in India
Why Choose the UK for Knee Replacement?
The UK is renowned for its high standards in medical care, particularly in orthopedic surgery. Here are a few reasons to consider the UK for knee replacement surgery:
2. Advanced Facilities: State-of-the-art hospitals with the latest technology.
3. Comprehensive Healthcare: Accessible, high-quality treatment through the NHS and private options.
4. Robust Rehabilitation: Comprehensive programs for quick recovery and regained mobility.
5. Research and Innovation: Leading in orthopedic research, offering the latest techniques and improved prosthetics.
6. Multidisciplinary Approach: Team of specialists providing personalized care.
Wellness Treatments
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
When is Knee Replacement Required?
Knee replacement surgery is usually recommended when:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of joint cartilage and underlying bone.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inflammatory disorder affecting the joints.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops after an injury.
Types of Knee Replacements
There are several types of knee replacement surgeries, each tailored to the patient's specific condition:
Total Knee Replacement involves replacing both sides of the knee joint. This procedure is typically recommended for patients with severe arthritis affecting the entire knee. By replacing damaged joint surfaces with artificial components, TKR offers comprehensive pain relief and significantly improved function, allowing patients to return to their daily activities with reduced discomfort and increased mobility.
Partial Knee Replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement, involves replacing only the damaged compartment of the knee. This option is suitable for patients whose knee damage is confined to a single area. Partial knee replacement is less invasive than total knee replacement, leading to a quicker recovery and retaining more natural knee function. This focused approach allows for targeted pain relief and improved joint movement.
Kneecap Replacement, or patellofemoral arthroplasty, involves replacing the under-surface of the kneecap and its groove. This procedure is recommended for patients with arthritis limited to the kneecap area. By addressing only the affected part of the knee, kneecap replacement provides focused treatment with a quicker recovery compared to total knee replacement, allowing patients to experience pain relief and enhanced knee function more rapidly.
Complex or Revision Knee Replacement is a more intricate procedure designed for patients who have severe arthritis or need a second knee replacement due to a failed previous surgery. This type of knee replacement addresses significant knee damage and complications from earlier procedures. Revision knee replacement aims to improve joint function, relieve pain, and restore mobility, offering a solution for complex cases that require specialized surgical expertise.
The Procedure
Pre-Operative Assessment
A thorough pre-operative assessment is crucial for ensuring the success of knee replacement surgery. This evaluation helps identify any potential risks, optimizes the patient's health, and prepares them for the procedure and recovery process. Here are the key components of a pre-operative assessment:
2. Diagnostic Tests:
Several diagnostic tests are conducted to provide detailed information about the condition of the knee and the patient's health status. These tests may include:
- X-rays: To assess the extent of joint damage and alignment issues.
- MRI Scan: To provide a detailed view of the knee’s soft tissues, if necessary.
- Blood Tests: To check for anemia, infection, and other health indicators.
3. Medication Review: A review of the patient’s current medications is essential to identify any that may need to be adjusted or stopped before surgery. Blood thinners, for instance, might need to be paused to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding during the procedure.
4. Health Optimization
Patients are advised to optimize their health in the weeks leading up to the surgery. This includes:
- Physical Fitness: Engaging in exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee.
- Dietary Adjustments: Maintaining a balanced diet to ensure optimal nutrition and healing.
- Weight Management: Reducing excess weight can decrease the stress on the knee and improve surgical outcomes.
5. Pre-Surgery Instructions: Patients receive detailed instructions on how to prepare for the surgery day. This includes guidelines on fasting, medication intake, and what to bring to the hospital. Understanding and following these instructions is vital for a smooth surgical experience.
6. Education and Counseling: Educating patients about the surgery, recovery process, and expected outcomes helps in setting realistic expectations. Counselling sessions might be provided to address any concerns or anxieties about the procedure.
7. Physical Therapy Planning: Meeting with a physical therapist before surgery can help patients learn exercises that will aid in their recovery. This pre-operative physical therapy can help build strength and flexibility, which will be beneficial post-surgery.
8. Home Preparation: Patients are advised to prepare their homes for post-operative recovery. This may involve arranging for mobility aids, setting up a comfortable recovery area, and organizing support from family or friends.
A thorough pre-operative assessment is vital for identifying any potential risks and ensuring that the patient is in the best possible condition for knee replacement surgery. By following the recommended guidelines and preparing adequately, patients can enhance their chances of successful surgery and a smooth recovery.
The Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, involves the removal of damaged joint surfaces and their replacement with artificial components. This procedure aims to relieve pain, restore function, and improve the quality of life for patients with severe knee joint damage. Here is an overview of what happens during the surgery:
1. Anaesthesia: The surgery begins with the administration of anaesthesia. Depending on the patient’s health and the surgeon’s recommendation, this may be either general anaesthesia (putting the patient to sleep) or regional anaesthesia (numbing the lower body while the patient remains awake).
2. Incision: Once the anaesthesia takes effect, the surgeon makes an incision, usually about 6 to 10 inches long, in the front of the knee to access the joint.
3. Preparation of the Joint
The damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). This step involves precise cutting and shaping of the bone to fit the prosthetic components accurately.
- Femoral Component: The end of the femur is resurfaced with a metal component.
- Tibial Component: The top of the tibia is fitted with a metal and plastic component.
- Patellar Component: If necessary, the under-surface of the kneecap is replaced with a plastic component.
These components are typically made of metal alloys, high-grade plastics, and polymers. They are fixed to the bone using specialized cement or a cementless method that allows the bone to grow into the implant.
5. Alignment and Balance: The surgeon meticulously aligns and balances the prosthetic components to ensure proper knee function and stability. This step is crucial for ensuring that the knee moves smoothly and that the ligaments and muscles function correctly.
6. Closure: After the prosthetic components are securely in place and the knee's function is tested, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples. A drain may be placed to remove excess fluid from the surgical site.
7. Post-Surgery Dressing: The knee is then bandaged and dressed to protect the wound and support the joint during the initial healing phase.
Recovery Process
Recovering from knee replacement surgery involves a comprehensive plan to ensure optimal healing and return to daily activities. Here is a detailed overview of the recovery process:
1. Hospital Stay: Patients typically stay in the hospital for 3 to 5 days post-surgery. During this time, medical staff monitor the patient’s condition, manage pain, and begin early rehabilitation.
2. Pain Management: Effective pain control is crucial for recovery. Pain relief is achieved through medications, which may include opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and local anesthetics. Pain management helps patients participate in physical therapy and perform necessary movements.
Short-Term Recovery (1 to 3 Months)
1. Physical Therapy:Regular physical therapy is essential for regaining strength, flexibility, and mobility. Therapy sessions focus on exercises that:
- Strengthen the muscles around the knee
- Improve range of motion
- Enhance balance and stability
- Gradually increase walking distance and endurance
3. Wound Care: Proper wound care is important to prevent infections. Patients are instructed on how to keep the surgical site clean and dry and to watch for signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
4. Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are scheduled to monitor the healing process, remove sutures or staples, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Long-Term Recovery (3 to 12 Months)
1. Continued Physical Therapy: Continued physical therapy helps patients regain full function of the knee. Exercises become more advanced, focusing on rebuilding muscle strength and joint stability, and preparing the patient for a return to normal activities, including low-impact sports.
2. Lifestyle Adjustments
Patients are encouraged to make lifestyle adjustments to protect the new joint and promote overall health. This includes:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee
- Engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, and walking
- Avoiding high-impact sports and activities that may damage the new joint
3. Pain and Swelling Management: Some residual pain and swelling may persist for several months. Patients are advised to use ice packs, elevate their leg, and take prescribed medications as needed to manage these symptoms.
The recovery process from knee replacement surgery is a structured and gradual journey that requires a commitment to physical therapy, proper wound care, and lifestyle adjustments. With diligent care and rehabilitation, patients can expect significant pain relief and improved knee function, leading to an enhanced quality of life.
Risks and Complications
While knee replacement surgery is generally safe and effective, like any major surgical procedure, it comes with certain risks and potential complications. Understanding these can help patients make informed decisions and manage their post-operative care effectively.
1. Infection: Infections can occur at the surgical site or around the prosthesis. Preventive measures, such as antibiotics and sterile surgical techniques, are used to minimize this risk. However, if an infection occurs, it may require additional treatment, including antibiotics or further surgery.
2. Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in the leg veins after surgery, potentially leading to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism if the clot travels to the lungs. Blood-thinning medications, compression devices, and early mobilization are typically used to prevent clots.
3. Implant Problems: Over time, the prosthetic components can wear out, become loose, or fail, which may require revision surgery. This is more common in younger, more active patients or those with high body weight, as these factors can increase the stress on the implant.
4. Persistent Pain: While most patients experience significant pain relief after knee replacement, some may continue to have pain. Persistent pain can result from various factors, including implant issues, improper alignment, or unaddressed sources of pain.
5. Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: During surgery, there is a small risk of injury to the nerves or blood vessels around the knee. This can lead to numbness, weakness, or circulatory issues in the affected leg. Such complications are rare but may require further medical attention.
6. Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion: Some patients may experience stiffness or limited range of motion in the knee after surgery. Physical therapy and exercise are essential to improving flexibility and strength, but in some cases, additional interventions may be needed to address severe stiffness.
7. Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some patients may have allergic reactions to the materials used in the prosthetic components. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, and inflammation around the joint. In such cases, alternative materials or treatments may be necessary
8. Anesthesia Risks: As with any surgery requiring anesthesia, there are risks associated with its use, including allergic reactions, respiratory issues, and complications related to pre-existing medical conditions. Anesthesia is administered and monitored by a specialized team to minimize these risks.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
Selecting a qualified and experienced surgeon is critical for a successful knee replacement:
- Research Credentials: Look for surgeons with specialized training in orthopedic surgery and significant experience in knee replacements.
- Patient Reviews: Consider feedback from previous patients regarding their experiences.
- Hospital Affiliation: Choose a surgeon affiliated with reputable hospitals.
- Consultations: Schedule consultations with multiple surgeons to find one you are comfortable with.
Knee replacement surgery can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with severe knee joint damage. It involves careful consideration, preparation, and a commitment to post-operative care and rehabilitation. With advancements in surgical techniques and prosthetic designs, patients in the UK can expect excellent outcomes and a return to active living. For those considering knee replacement surgery, it's essential to consult with an orthopedic specialist to discuss individual needs, options, and expected outcomes.
Related Blogs
Compare Neuro Surgery Costs Across Cities with Healthtrip’s Help
Find everything you need to know about neuro surgery in

Find the Best Doctor for Neuro Surgery in India with Healthtrip
Find everything you need to know about neuro surgery in
Steps to Prepare for Your Neuro Surgery with Healthtrip in India
Find everything you need to know about neuro surgery in
Why International Patients Prefer Healthtrip for Neuro Surgery in India
Find everything you need to know about neuro surgery in

Top Patient Concerns About Neuro Surgery and How Healthtrip Addresses Them
Find everything you need to know about neuro surgery in

Get Personalised Care for Neuro Surgery with Healthtrip’s Partner Hospitals
Find everything you need to know about neuro surgery in










